From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This article is about the biological organ. For other uses, see Heart (disambiguation).
"Cardiac" redirects here. For the cardboard computer, see CARDboard Illustrative Aid to Computation.
 |
Sorry, your browser either has JavaScript disabled or does not have any supported player.
You can download the clip or download a player to play the clip in your browser.
Normal heart sounds as heard with a stethoscope
|
| Problems listening to this file? See media help. | |
Real-time MRI of the human heart
The heart is a hollow muscle that pumps blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. It is found in all animals with a circulatory system (including all vertebrates).[1]
The term cardiac (as in cardiology) means "related to the heart" and comes from the Greek καρδιά, kardia, for "heart".
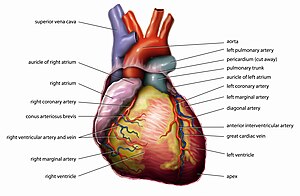
The vertebrate heart is principally composed of cardiac muscle and connective tissue. Cardiac muscle is an involuntary striated muscle tissue found only in this organ and responsible for the ability of the heart to pump blood.
The average human heart, beating at 72 beats per minute, will beat approximately 2.5 billion times during an average 66 year





0 التعليقات:
إرسال تعليق
ملحوظة: يمكن لأعضاء المدونة فقط إرسال تعليق.